USGS Nebraska Water Science Center
Publications
USGS publications, including those from the USGS Nebraska Water Science Center, are available through the USGS Publications Warehouse. USGS authors publish in many of the same outlets as researchers in academia, but also publish in USGS-series reports that are publically-available. Our most recent publications are shown below.
By Virginia L. McGuire
The High Plains aquifer underlies 111.8 million acres (about 175,000 square miles) in parts of eight States—Colorado, Kansas, Nebraska, New Mexico, Oklahoma, South Dakota, Texas, and Wyoming. Water-level declines began in parts of the High Plains aquifer soon after the beginning of substantial irrigation with groundwater in the aquifer area (about...
By Virginia L. McGuire
The High Plains aquifer underlies 111.8 million acres (about 175,000 square miles) in parts of eight States—Colorado, Kansas, Nebraska, New Mexico, Oklahoma, South Dakota, Texas, and Wyoming. More than 95 percent of the water withdrawn from the High Plains aquifer is used for irrigation. Water-level declines began in parts of the High Plains...
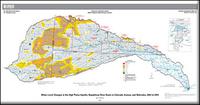
By Steven M. Peterson, Amanda T. Flynn, Jonathan P. Traylor
The High Plains aquifer is a nationally important water resource underlying about 175,000 square miles in parts of eight states: Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, Nebraska, New Mexico, South Dakota, Texas, and Wyoming. Droughts across much of the Northern High Plains from 2001 to 2007 have combined with recent (2004) legislative mandates to elevate...
Flood-inundation maps for a 12.5-mile reach of Big Papillion Creek at Omaha, Nebraska
By Kellan R. Strauch, Benjamin J. Dietsch, and Kayla J. Anderson
Digital flood-inundation maps for a 12.5-mile reach of the Big Papillion Creek from 0.6 mile upstream from the State Street Bridge to the 72nd Street Bridge in Omaha, Nebraska, were created by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) in cooperation with the Papio-Missouri River Natural Resources District. The flood-inundation maps, which...
By Nathaniel J. Schaepe, Jason S. Alexander, and Kiernan Folz-Donahue
The Niobrara River is an important and valuable economic and ecological resource in northern Nebraska that supports ecotourism, recreational boating, wildlife, fisheries, agriculture, and hydroelectric power. Because of its uniquely rich resources, a 122-kilometer reach of the Niobrara River was designated as a National Scenic River in 1991, which has...
Water balance monitoring for two bioretention gardens in Omaha, Nebraska, 2011–14
By Kellan R. Strauch, David L. Rus, Kent E. Holm
Bioretention gardens are used to help mitigate stormwater runoff in urban settings in an attempt to restore the hydrologic response of the developed land to a natural predevelopment response in which more water is infiltrated rather than routed directly to urban drainage networks. To better understand the performance of bioretention...